Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

NADPH tetrasodium salt is the reduced form of the electron acceptor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, which acts as an electron donor in a variety of biological reactions. NADPH tetrasodium salt is also an endogenous inhibitor of ferroptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $65 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $98 | In Stock |
| Description | NADPH tetrasodium salt is the reduced form of the electron acceptor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, which acts as an electron donor in a variety of biological reactions. NADPH tetrasodium salt is also an endogenous inhibitor of ferroptosis. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Neurons were pretreated with NADPH tetrasodium salt (2.5-10 μM) for 1-8 h, then treated with Kainic acid (KA, 100 μM) for 8 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay.
RESULTS: KA treatment significantly reduced the cell viability of primary cortical neurons in a time-dependent and dose-dependent manner, and NADPH pretreatment significantly promoted neuronal survival, which was more effective at 10 μM for 4 or 8 h. The RESULTS showed that Kainic acid (KA, 100 μM) treatment significantly reduced the cell viability of primary cortical neurons. [1] METHODS: Neurons were pretreated with NADPH tetrasodium salt (10 μM) for 4 h, and then treated with Kainic acid (KA, 100 μM) for 8 h. The expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: The expression of TIGAR was decreased after KA treatment, and it was significantly reversed by NADPH. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To examine the effects on Kainic acid (KA)-induced excitotoxicity and its mechanism, NADPH tetrasodium salt (1-2 mg/kg in saline) was administered intravenously to KA-induced rats once a day for seven days.
RESULTS: NADPH reduced KA-induced increase in striatal lesion size, improved KA-induced dyskinesia, and reversed KA-induced glial cell activation. [1] METHODS: NADPH tetrasodium salt (2.5 mg/kg) was intravenously injected into ICR mice to determine whether exogenous NADPH could enter the brain tissues and neurons of mice. RESULTS: Injection of NADPH significantly increased the levels of NADPH in the blood and brain tissue of mice.The half-life of NADPH in the blood of mice is about 6 h and in the brain tissue is 7 h. [2] |
| Molecular Weight | 833.35 |
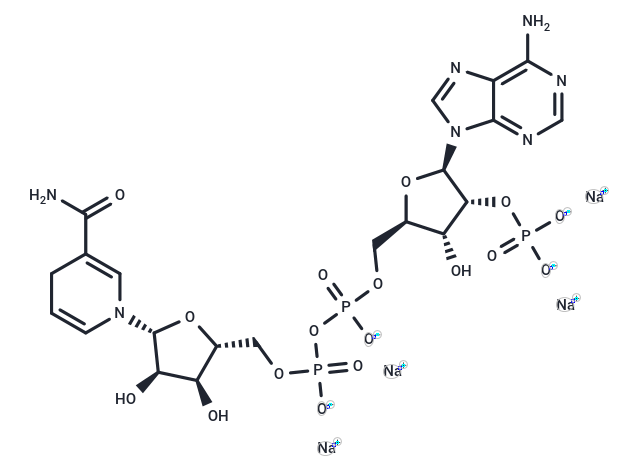
| Formula | C21H26N7Na4O17P3 |
| Cas No. | 2646-71-1 |
| Smiles | [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].NC(=O)C1=CN(C=CC1)[C@@H]1O[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OP([O-])(=O)OC[C@H]2O[C@H]([C@H](OP([O-])([O-])=O)[C@@H]2O)n2cnc3c(N)ncnc23)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 2.28 g/cm C |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.25 mg/mL (1.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 35 mg/mL (42 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.